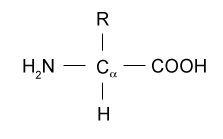
The 9 essential amino acids are histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionineGuanidine Acetic Acid (GAA)can improve the lean meat rate, promote the growth of animals, and reduce the input of feed Guanidine acetic acid is the only source of creatine synthesis in animals, such as poultry, cattle, sheep, pigs and so on Due to the limited ability of animals to synthesize guanidine acetic acid, it is easy to lead to the lack of creatine in vivo, so it needs to supplement amino acid and proteins The amino acid that is detected in this test is arginine Since arginine has a guanidine group in its side chain Christian Cauilan Pacquing RESULT Christian Cauilan Pacquing NITROPRUSSIDE TEST • The nitroprusside test is specific for cysteine, the only amino acid containing sulfhydryl group

Solved 1 Which Amino Acids Contain The Following A Chegg Com
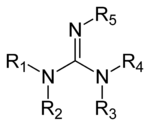
Which amino acids contain guanidine group
Which amino acids contain guanidine group-Millon's test How many of the amino acids are essential? Interaction between the guanidinium cation and aromatic amino acids RodríguezSanz AA(1), CabaleiroLago EM, RodríguezOtero J Author information (1)Departamento de Química Física, Facultade de Ciencias, Universidade de Santiago de Compostela, Campus de Lugo Avda Alfonso X El Sabio s/n, Lugo, Spain cabalago@usces The interaction of the




Arginine Duluth Labs
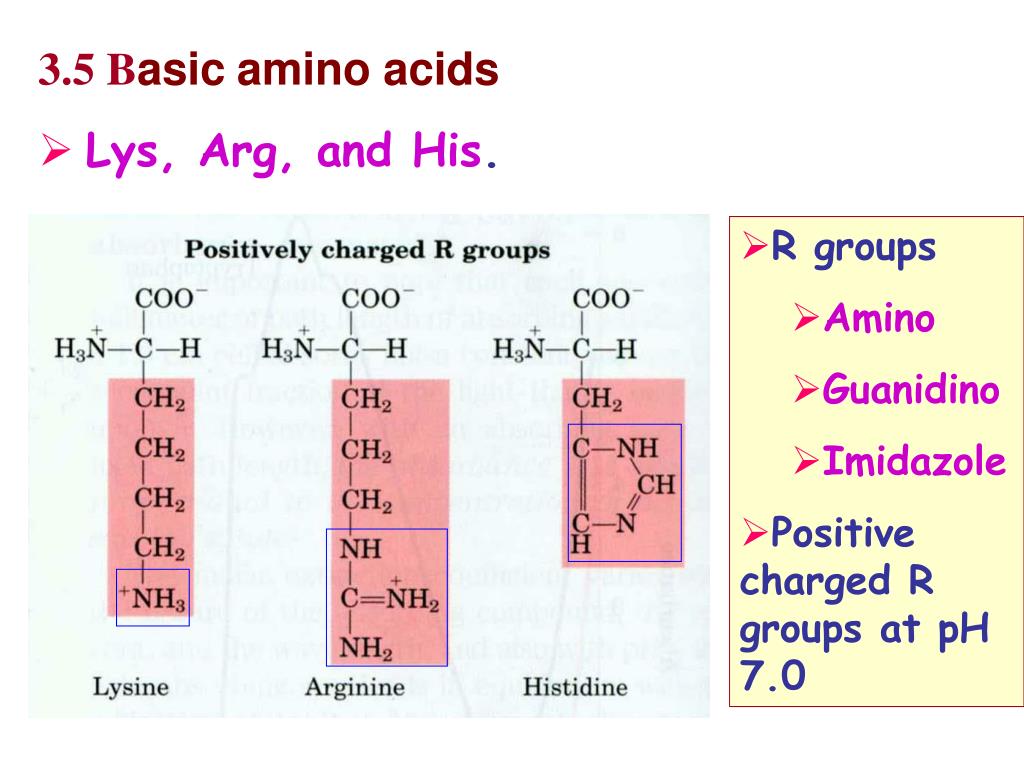
They are lysine, which has a butylammonium side chain, arginine , which has a guanidine group, and histidine, which bears an imidazolium moietyAlso to know is, which amino acids contain guanidine?Synthesis of Guanidine Amino Acids and Investigation of their Interactions with Nucleic Acid Thesis submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy by Vicki Doreen Möschwitzer Supervisor Dr James E Redman School of Chemistry Cardiff University July 11
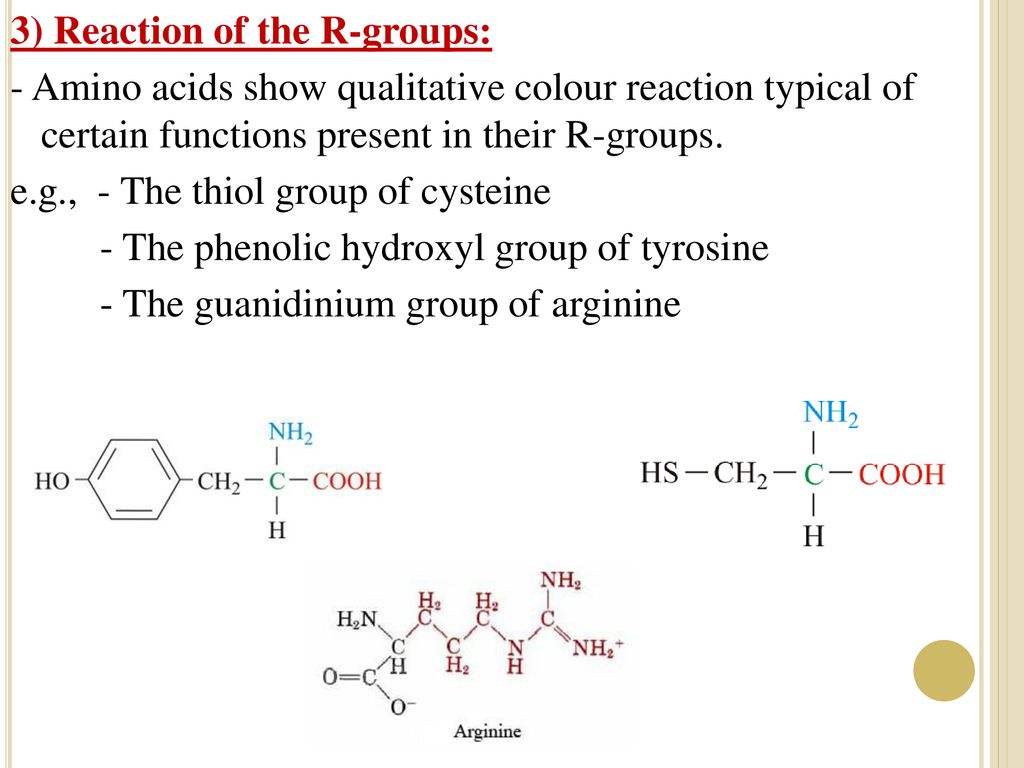
The only amino acid containing the guanidine group is arginine, and this reacts with a naphthol and an oxidizing agent such as bromine water or sodium hypochlorite to give a red coloured product The other guanidine containing nonamino acid compounds also give this reaction Materials and Reagents 1 Amino acids 01% solution of amino acids like glycine, arginine,A sulfur/sulfhydryl group b aromatic group c imidazole ring d guanidine group e indole group a sulfur/sulfhydryl group b aromatic group c imidazole ring d guanidine group e indole group Basic Amino Acids Definition Basic amino acids are those amino acids that have an amino group on their side chains at neutral pH, resulting in basic or alkaline properties in the molecule Basic amino acids have an additional amino group (NH 2) in addition to the one present in the central chain
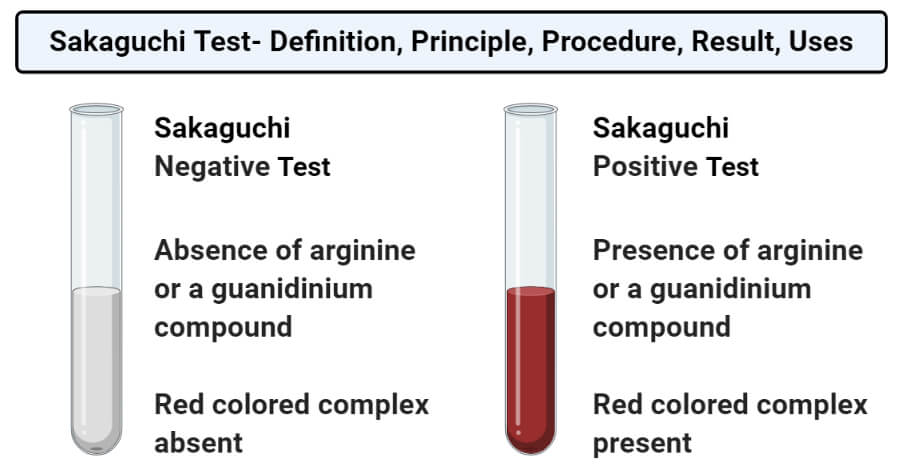
Li and Brill postulate that the guanidine group in arginine is hydrolyzed into a terminal amino group, that is, ornithine is produced, consequently together with urea as illustrated in Scheme 6 30 Urea is known to decompose quickly into CO 2 and ammonia under hydrothermal conditions 38 Ornithine is assumed to form a sixmembered lactam by the condensation of the terminal amino groupSakaguchi's test is positive for the amino acid containing the guanidine group in Arginine Guanidine group present in the amino acid reacts with αNaphthol and alkaline hypobromite to give redcoloured complex Procedure & observation − To 1 mL of protein solution in a test tube, add 40%NaOH (23 drops) Ethanolic aNaphthol (23 drops) and Bromine water (23 drops) −They are lysine, which has a butylammonium side chain, arginine , which has a guanidine group, and histidine, which bears an imidazolium moiety




Statement 1 Arginine I Is The Most Basic Out Of Twenty Common Amino Acids H 2 N Underset Underset Nh C Nh Ch 2 Ch 2 Ch 2 Underset Underset Nh 2 Ch Cooh Statement 2 Arginine Contains Guanidine Group Whose Protonated Cation



Sakaguchi Test Principle Reaction Reagents Procedure And Result Interpretation Online Biochemistry Notes
Since arginine has a guanidine group in its side chain, it gives a red color with αnaphthol in the presence of an oxidizing agent like bromine solution Which of the following test is used to detect the presence of phenolic amino acids?Indolo2,3bquinoline) and a guanidine group, an amino acid residue or an Nguanylamino acid All new conjugates were tested for their cytotoxic activity against cancer and normal cell lines and against fungal biofilms as well as for their DNA interactions Most promising compounds were selected to establish their mechanism of action Moreover, all novel conjugates were tested forThe highly stereoselective supramolecular selfassembly of αamino acids with a chiral aldehyde derived from binol and a chiral guanidine derived from diphenylethylenediamine (dpen) to form the imino acid salt is reported This system can be used to cleanly convert Damino acids into Lamino acids or vice versa at ambient temperature It can also be used to synthesize αdeuterated D or



Solved Acid Base Behavior Of Amino Acids Guanidine And The Guanidino Group Present In Arginine Are



Chiral Guanidines And Their Derivatives In Asymmetric Synthesis Chemical Society Reviews Rsc Publishing
Five amino acids contribute to this type The side chains are positively charged;1) a Sulfur/sulfhydryl group = methionine, cysteine, homocysteine b Aromatic group= phenylalanine, tyrosine, tryptophan c Imidazole ring= histidine d Guanidine group= arginine e Indole group= view the full answerFrom what are derived amino acids?ChemInform Abstract Synthesis of Novel Modified Guanidines Reaction of Dicyandiamide with Amino Acids, Amides, The amino acid that is detected in this test is arginine Since arginine has a guanidine group in its side chain, it gives a red color with αnaphthol in the presence of an oxidizing agent like bromine solution What is unique about proline?




Ii Protein Biochemistry 2 1 Amino Acids 2



Guanidino Is Present In The Amino Acid Class 12 Chemistry Cbse
GuanidineBased γPeptide Nucleic Acids γ from the firstgeneration GPNAs in that the guanidinium group is installed at the γ instead of the Rposition of the N(2aminoethyl)glycine backbone unit This positional switch enables GPNAs to be synthesized from relatively cheap L as opposed to Damino acids Unlike their Rpredecessors, which are randomly folded, γGPNAsWhich amino acids contain the following?Guanidine is not expected to undergo hydrolysis in the environment due to the lack of functional groups that hydrolyze under environmental conditions(2) Guanidine does not contain chromophores that absorb at wavelengths >290 nm and therefore is not expected to be susceptible to direct photolysis by sunlight(2)



Week 1 Amino Acids Prof Sbw Ppt Download




Guanidinium An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
1 Amino AcidProtecting Groups Albert IsidroLlobet,1 Mercedes Álvarez,1,2,3* Fernando Albericio1,2,4* 1Institute for Research in Biomedicine, Barcelona Science Park, Baldiri Reixac 10, Barcelona, Spain 2CIBERBBN, Networking Centre on Bioengineering, Biomaterials and Nanomedicine, Barcelona Science Park, Baldiri Reixac 10, Barcelona, SpainA sulfur/sulfhydryl group b aromatic group c imidazole ring d guanidine group e indole group 2 Classify the following proteins according to their biological function casein, albumin gluten, and myoglobin 3 Which levels of protein structure organization are lost during hydrolysis and denaturation? Two activations are better than one The chiral bifunctional guanidine 1, which features an amino amide backbone, catalyzes the asymmetric Michael addition of a range of substrates and gives products with excellent stereoselectivities The method also allows the efficient synthesis of optically pure β‐amino acid esters Both the guanidine group and the NH




Guanidine Guanidinium Chloride Arginine Hydrochloride Barytwasser Others Angle Text Logo Png Pngwing




Guanidine And Guanidinium Cation In The Excited State Theoretical Investigation The Journal Of Chemical Physics Vol 141 No 7
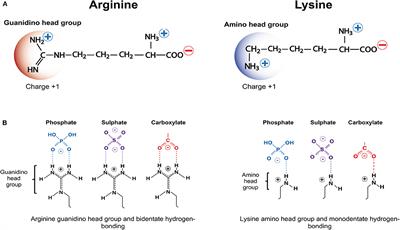
The amino acid side chain of arginine contains a guanidino groups and, similar to lysine, carries a positive charge It is often found solvent exposed on the surfaces of proteins and thus readily accessible to glycation reagents Because the guanidino group contains two reactive nitrogens, rather than only one as in the lysine side chain, it shows a more diverse chemistry Reaction withProline is unique in that it is the only amino acid where the side chain is connected to the protein backbone twice, forming a fivemembered The amino acid which contains a guanidine group is (A) Histidine (B) Arginine Citrulline (D) Ornithine Login




Effect Of Each Guanidinium Group On The Rna Recognition And Cellular Uptake Of Tat Derived Peptides Sciencedirect
/E103845A0673B57E802585FA0046E46C/$file/IB57827_structure.png)



1 3 Bis P Chlorobenzylidene Amino Guanidine Hydrochloride 50 7 Biosynth Carbosynth
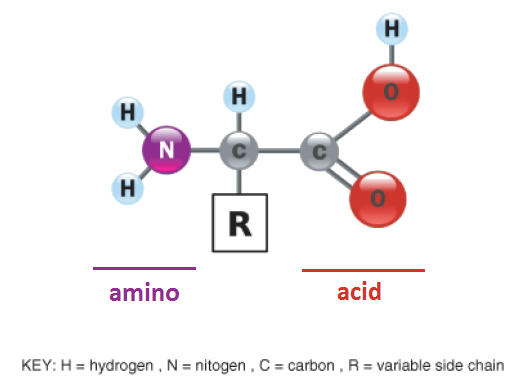
Which amino acids contain guanidine?Guanidoacetic acid exists naturally in all vertebrates It is formed primarily in the kidneys by transferring the guanidine group of Larginine to the amino acid glycine via the enzyme known as LArgGlyamidinotransferase (AGAT) In a further step, guanidinoacetate is methylated to generate creatine using Sadenosyl methionine (as the methylAmino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side chain that varies betwen different amino acids Amino acids of the general formula RCH(NH 2)COOH are amphoteric, behaving as amines in some reactions and as carboxylic acids in others At a certain pH known as the isoelectric point an amino acid has no overall charge, since the number of




Solved 1 Which Amino Acids Contain The Following A Chegg Com



Development Validation Of A Gc Ms Method For The Simultaneous Measurement Of Amino Acids Their Ptm Metabolites And Ages In Human Urine And Application To The Bi Ethnic Asos Study With Special Emphasis To
Guanidine Acetic Acid (GAA)can help to reduce the fat thickness of the back fat of cattle and sheep, make the gluteus and leg muscles of raw cattle and sheep developed and full, the body shape plump and strong, improve the quality of ketone body, and improve the rate of leanArginine, an essential amino acid, has a positively charged guanidino group Arginine is well designed to bind the phosphate anion, and is often found in the active centers of proteins that bind phosphorylated substrates As a cation, arginine, as well as lysine, plays a role in maintaining the overall charge balance of a proteinGuanidine moieties represented as hydrophilic functional groups are also present in the sidechain arginine amino acid, which has been observed in various enzyme active sites and motifs of cell



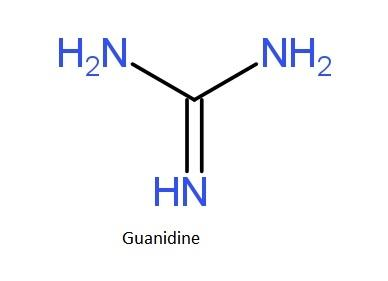
Guanidine Wikipedia



Frontiers Cationic Arginine Rich Peptides Carps A Novel Class Of Neuroprotective Agents With A Multimodal Mechanism Of Action Neurology
Are Branched Chain Amino Acid used to prevent muscle loss and increase muscle mass Isoleucine (Ile,I) Leucine (Leu,L) Valine (Val,V) A derivative of glutamic acid as a flavor enhancer4 What is the BeerLambert's Law?Indeed, both the guanidine group of arginine and the two triterpenoid acids are items known for directing antibacterial effects, particularly against Grampositive bacteria The cationic dendrimers were obtained by peripheral conjugation with the selected amino acids and by entrapping a physical mixture of the commercial triterpenoid acids The cationic compounds were




Explain Why When The Guanidino Group Of Arginine Is Protonated The Double Bonded Nitrogen Is The Brainly Com



Sakaguchi Test Definition Principle Procedure Result Uses
There are basically standard amino acids having different structures in their side chains(R groups) The common amino acids are known as aamino acids because they have a primary amino group(NH2) and a carboxylic acid group(COOH) as substitutes of the a carbon atoms Proline is an exception because it has a secondary amino group (NH), for uniformity it is also treated as alphaamino acidSakaguchi's test is positive for the amino acid containing the guanidine group in Arginine Guanidine group present in the amino acid reacts with αNaphthol and alkaline hypobromite to give redcoloured complex Procedure & observation − To 1 mL of protein solution in a test tube, add 40%NaOH (24 drop) Ethanolic aNaphthol (2 drops) and Bromine water (510 drops) − contain two amino groups, hence called dibasic monocarboxylic acids Highly basic in nature Lysine (K), Arginine (R) (with guanidine group) and Histidine (H)(with imidazole ring



2



2
It has an amide group An aromatic amino acid It has a phenol group Polar Amino Acids (Positively Charged = Basic) Name Abbreviation Structure Features It has an amine(o) group (in the Rgroup) It has a guanidine(o) group group It has an imidazole group It has a buffering importance Polar Amino Acids (Negatively Charged =Which amino acids contain the following?Guanidine groups within a nonpolymeric hydrophilic molecular system was suspected to be the chemical structure of streptomycin implicated in the interaction with proteins1 This interaction takes place through hydrogen bond transfer among the 2 guanidine groups on streptomycin and the aminoacids of one or several prion peptides The




Pdf A New Method To Synthesize Creatine Derivatives Annalisa Salis Patrizia Garbati And Enrico Millo Academia Edu




Time And Nadph Dependent Inhibition Of Cytochrome P450 3a4 By The Cyclopentapeptide Cilengitide Significance Of The Guanidine Group And Accompanying Spectral Changes Drug Metabolism Disposition
Kinds of groups constituting the protein molecule This assump tion is also applied to small model compounds, so that an ap 1650 Solubility of Amino Acids in Aqueous Guanidine Hydrochloride Vol 245, No 7 TABLE IV Contributions of peptide unit (Af'f't) to free energy of transfer at 261" Af't at GuHCl concentration of From AF't values of cal/mol e Diglycine, glycine 85 1Amino acids are a group of organic compounds containing two functional groups amino and carboxyl The amino group (NH2) is basic while the carboxyl group (COOH) is acidic in nature The general structure of amino acids The amino acids are termed as aamino acids If both the carboxyl and amino groups are attached to the same carbon atom, as It is noteworthy that many of the reported methods do not show generality, especially for amino acids and peptides, without using additive11, 14, 28 In conclusion, we have shown that Gu·HCl can be used as an efficient catalyst for selective and chemoselective NBoc protection of amines, diamines, amino acids and peptides The catalyst can be recovered and reused in the




The Biosynthesis Of Methylated Amino Acids In The Active Site Region Of Methyl Coenzyme M Reductase Journal Of Biological Chemistry




White Paper High Purity Low Endotoxin Arginine Applications In Biopharmaceutical Processing Biotherapeutic Stabilization
PKa and pI values of amino acids Amino acid 3letter code 1letter code pKa CαCOOH pKa CαNH 3 pKa side chain Isoelectric point (pI) Alanine Ala A 234 969 602 Arginine Arg R 217 904 1248 1076 Asparagine Asn N 2 0 541 Aspartic acid Asp D 9 9 386 298 Cysteine Cys C 171 1078 3 502 Glutamic acid Glu E 219 967 425 322 Glutamine Gln Q 217 913 Two activations are better than one The chiral bifunctional guanidine 1, which features an amino amide backbone, catalyzes the asymmetric Michael addition of a range of substrates and gives products with excellent stereoselectivitiesThe method also allows the efficient synthesis of optically pure βamino acid esters Both the guanidine group and the NH proton ofChemical structure of three amino acids with guanidinium group guanidine hydrochloride, arginine monohydrochloride, and creatinine



Illustrated Glossary Of Organic Chemistry Guanidine




Guanidinium Salt An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Five amino acids contribute to this type The side chains are positively charged;The guanidinium functional group is commonly used by proteins and enzymes to recognize and bind anions using ion pairing and hydrogen bonding The specific patterns of hydrogen bonding and the great basicity of the guanidine functional group allow it to play several key roles in recognition and catalysis This chapter outlines recent findings of guanidinium groups in natural systems andChemical modification of amino groups and guanidino groups of trypsin Preparation of stable and soluble derivatives Nureddin A, Inagami T 1 Isoionic chemical modification of amino groups of trypsin (EC ) was studied for the purpose of obtaining a welldefined modified trypsin with minimum changes in physicochemical properties and with sufficient stability at neutral pH



Amino Acids Amino Acids Ppt Download



Sakaguchi Test Principle Reaction Reagents Procedure And Result Interpretation Online Biochemistry Notes
The reaction could be easily scaled up under mild conditions to facilitate a concise synthesis of a bicyclic β‐amino acid The comparative experiments and X‐ray diffraction analysis of the catalyst structures revealed both the guanidine group and the NH proton of the amide are important for the dual‐activation mode Experimental Section β‐Ketoester 6 b (276 mg, 015 mmol) was added to a stirred solution of nitroolefin (133 equiv, 02 mmol) and guanidine The only amino acid containing the guanidine group is arginine Therefore this test is specific for identification of arginine Arginine reacts with αnaphthol in presence of an oxidizing agent such as bromine water or sodium hypochlorite to give a red coloured product The other guanidine containing nonamino acid compounds also give this reaction Reaction Reagents Test solutions AminoThe amino acid arginine Arginine is an amino acid that has a guanidine group in its side chain, which is the C atom that binds N2 with a single bond and binds N with a double bond Sakaguchi reaction is carried out using naphthol and sodium hypobromite or sodium hypochlorite reagents The guanidine




Synthesis Of Guanidinium Modified Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel Varghese 10 Macromolecular Rapid Communications Wiley Online Library
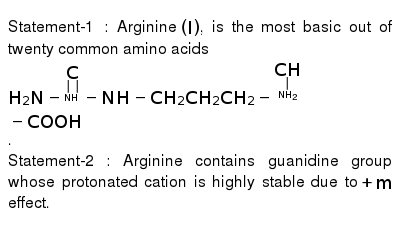



Statement 1 Arginine I Is The Most Basic Out Of Twenty Common Amino Acids H 2 N Underset Underset Nh C Nh Ch 2 Ch 2 Ch 2 Underset Underset Nh 2 Ch Cooh Statement 2 Arginine Contains Guanidine Group Whose Protonated Cation
Amino Acids Lysine Other protecting group Boc Amine PGs Introduction Cbz 2 O, Cbz‐Cl Alloc 2 O, Alloc‐Cl ivDde‐OH Removal H 2 Pd(PPh 3), PhSiH 3 2% N 2 H 4 Stable Basic and Acidic conditions Basic and Acidic conditions Basic and Acidic conditions, Hydrogenation Orthogonal Boc, Fmoc, Trt Boc, Fmoc, Trt Boc, Fmoc, Z, Trt, Alloc 4 For α‐carboxylic acids, Aspartic and Glutamic Acid




Guanidino Group An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Arginine Wikipedia




Glycocyamine Used As A Supplement A Metabolite Of Glycine In Which The Amino Group Has Been Converted Into A Guanidine Canstock



Chiral Guanidines And Their Derivatives In Asymmetric Synthesis Chemical Society Reviews Rsc Publishing




Arginine Duluth Labs



Molecules Free Full Text Synthetic Approaches To A Challenging And Unusual Structure An Amino Pyrrolidine Guanine Core Html



Sensors Free Full Text Evaluation Of Metal Oxide Surface Catalysts For The Electrochemical Activation Of Amino Acids Html




Color Test For Proteins And Amino Acids Proteins



2



Guanidine A Simple Molecule With Great Potential From Catalysts To Biocides And Molecular Glues



Exam 3 Answer Key




Morphological And Conformational Analysis Of H Ttl Aggregates A Download Scientific Diagram



Amino Acids Arginine R Arg



The Bowers Group University Of California At Santa Barbara




Positively Charged Amino Acids Arginine And Lysine And Hydrogen Download Scientific Diagram




Proteins Proteins Are A Complex Nitrogenous Group With High Molecular Weight It Consist Of A Large Number Of Amino Acid Connected Together With A Special Ppt Download




Recent Advances In Guanidine Based Organocatalysts In Stereoselective Organic Transformation Reactions Intechopen




Exceptionally Versatile Arginine In Bacterial Post Translational Protein Modifications



In Vitro Modification Of Bacterial Cyanophycin And Cyanophycin Dipeptides Using Chemical Agents Towards Novel Variants Of The Biopolymer Springerlink



3
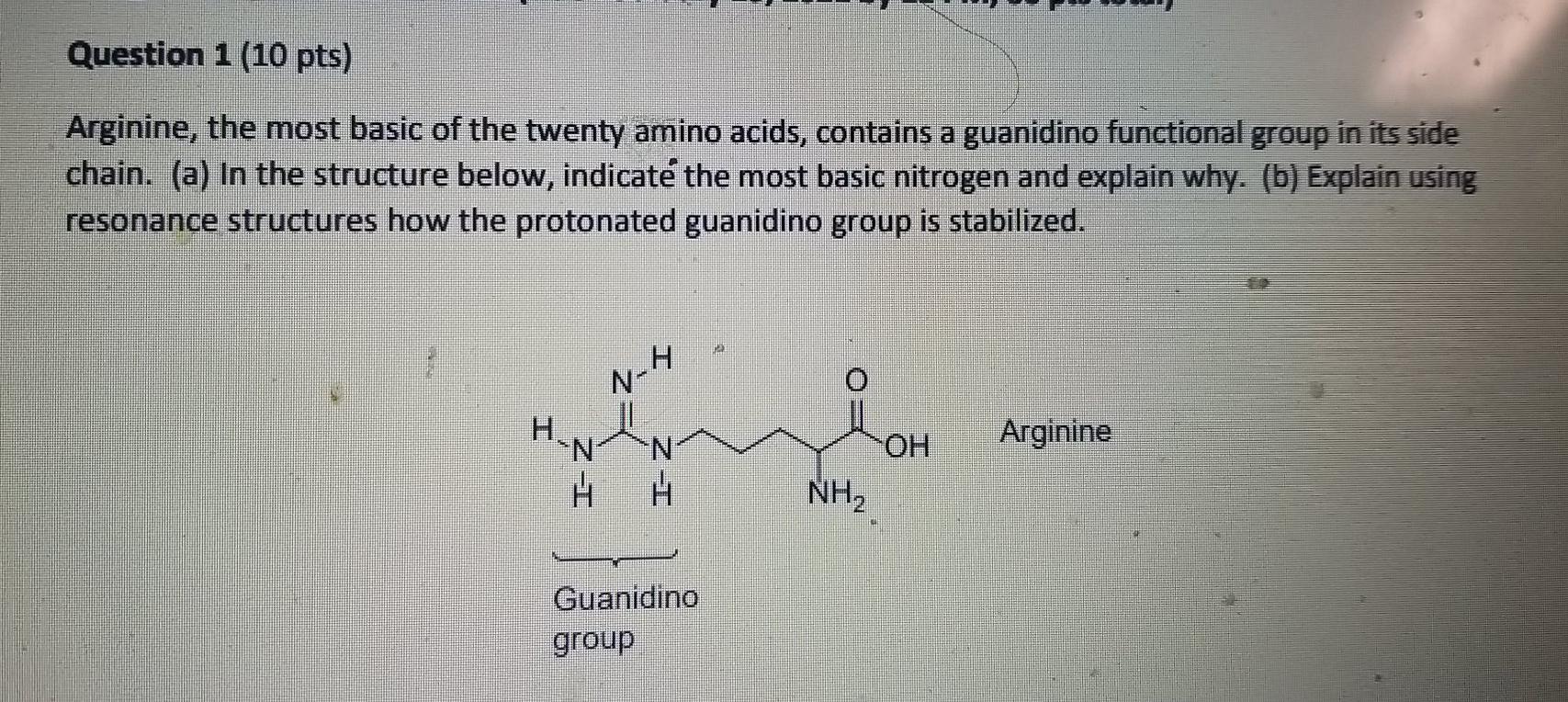



Solved Question 1 10 Pts Arginine The Most Basic Of The Chegg Com




Color Test For Proteins And Amino Acids Proteins




Lab Activity 8 Proteins 2 Alaa S Baraka Islamic University Of Gaza March Ppt Download



1



Amino Acids A Functional Group Biology Ease




Guanidinium Chloride Wikipedia
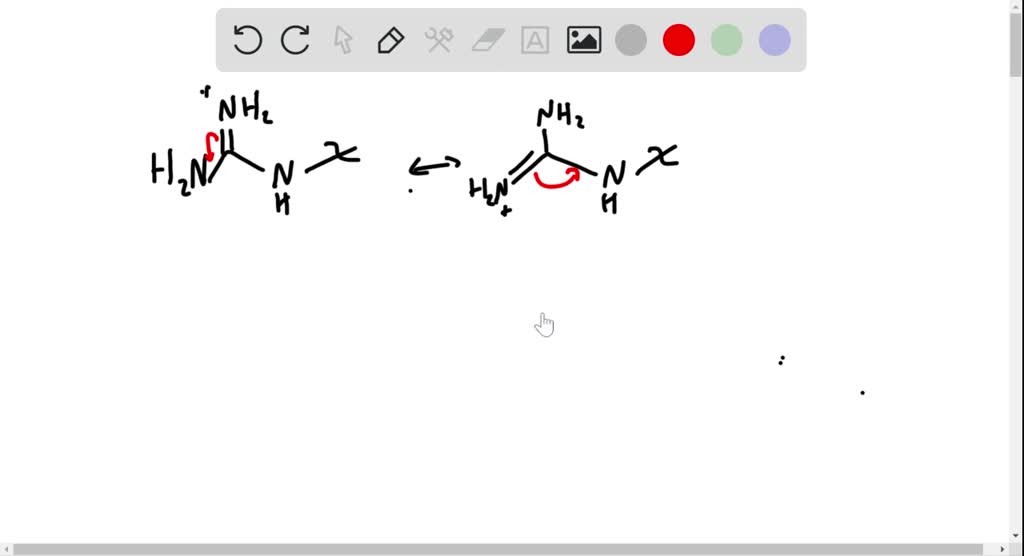



Solved Arginine The Most Basic Of The Common Amino Acids Contains A Guanidino Functional Group In Its Side Chain Explain Using Resonance Structures To Show How The Protonated Guanidino Group Is Stabilized




Learnbiochemistry Aminoacid Aminoacids Biochemistry Biochemistrymcq Biochemistrystudent Learnbiochemistry Facebook
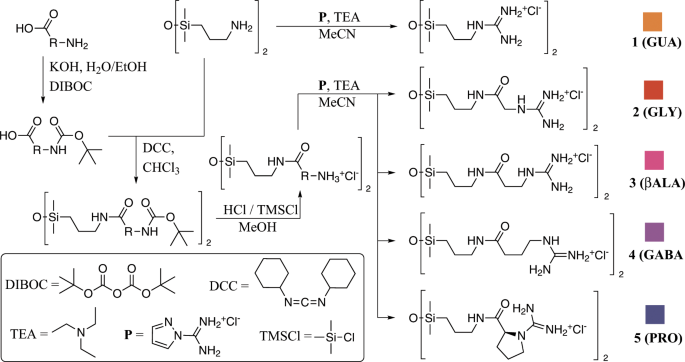



Exploring Ion Ion Preferences Through Structure Property Correlations Amino Acid Derived Bis Guanidinium Disiloxane Salts Scientific Reports



1




Urea But Not Guanidinium Destabilizes Proteins By Forming Hydrogen Bonds To The Peptide Group Pnas




Guanidine Wikipedia



Ppt Lecture 1 Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Guanidinium Group A Versatile Moiety Inducing Transport And Multicompartmentalization In Complementary Membranes Sciencedirect




Deprotonation Reaction Of Arginine In The Gas Phase R Means The Download Scientific Diagram
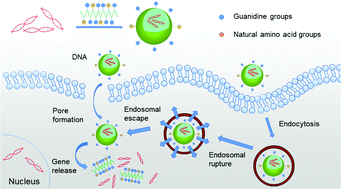



Guanidine Rich Helical Polypeptides Bearing Hydrophobic Amino Acid Pendants For Efficient Gene Delivery Biomaterials Science Rsc Publishing



Guanidino Is Present In The Amino Acid Class 12 Chemistry Cbse



Mechanistic Considerations Of Guanidine Catalyzed Reactions Chemical Communications Rsc Publishing




Amino Guanidine Energeticchemical




Solved Creatine And Arginine Are Two Amino Acids Containing Chegg Com



Mcq On Protein Structure Amino Acid Mcq With Answers Pdf Jobsjaano Com
/63589E4AF83B1572802585F9006F4B6A/$file/FG09296_structure.png)



Guanidine Hcl 50 01 1 Biosynth Carbosynth



Guanidine A Simple Molecule With Great Potential From Catalysts To Biocides And Molecular Glues




Guanidine Formula Uses Facts Britannica



2




Guanidine Group Guanidine Functional Group 約ネバ エマ アニメ画像




Welcome To Chem Zipper Com What Is Guanidine And Its Structure Name Amino Acid Which Contains Guanidine Group



Amino Acids And Proteins
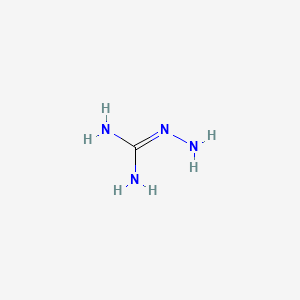



Aminoguanidine Ch6n4 Pubchem
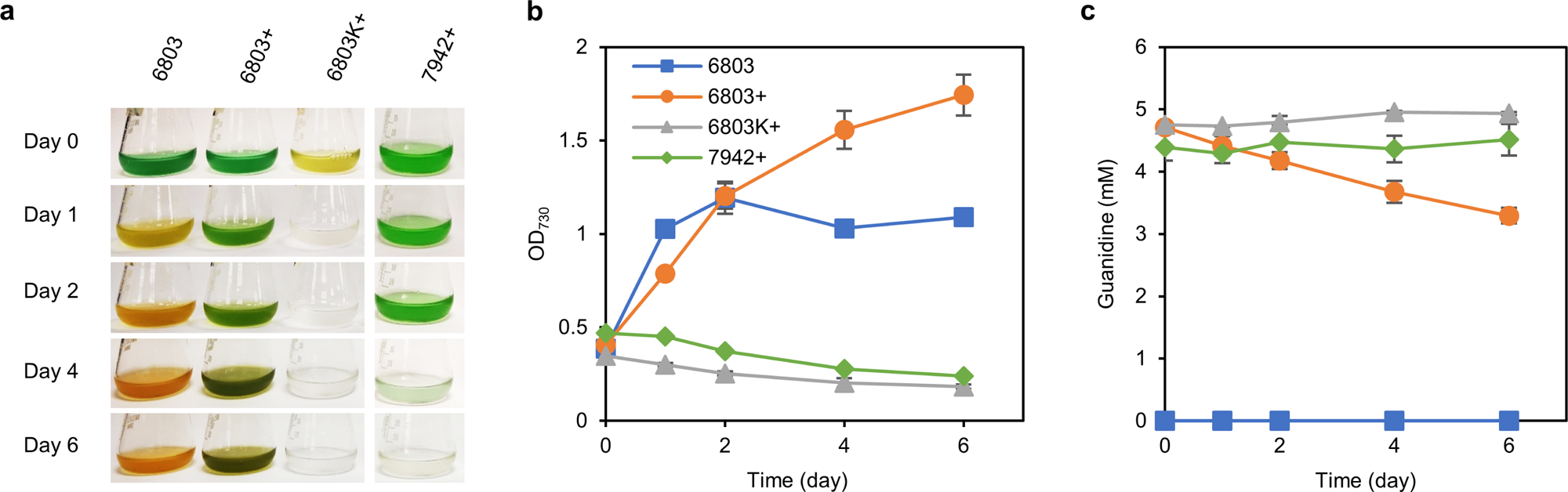



A Guanidine Degrading Enzyme Controls Genomic Stability Of Ethylene Producing Cyanobacteria Nature Communications



Amino Acids




Amino Acid Amino Acid Amino Acid Peptide Linkage Proteins Many Peptide Linkages Pdf Free Download




Deprotonation Reaction Of Arginine In The Gas Phase R Means The Download Scientific Diagram




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader



2



Guanidine Group Guanidine Functional Group 約ネバ エマ アニメ画像




Classical Guanidine Synthesis Guanidine Core Structure Obtained By Download Scientific Diagram




Recent Advances In Guanidine Based Organocatalysts In Stereoselective Organic Transformation Reactions Intechopen




Modification And Functionalization Of The Guanidine Group By Tailor Made Precursors Protocol
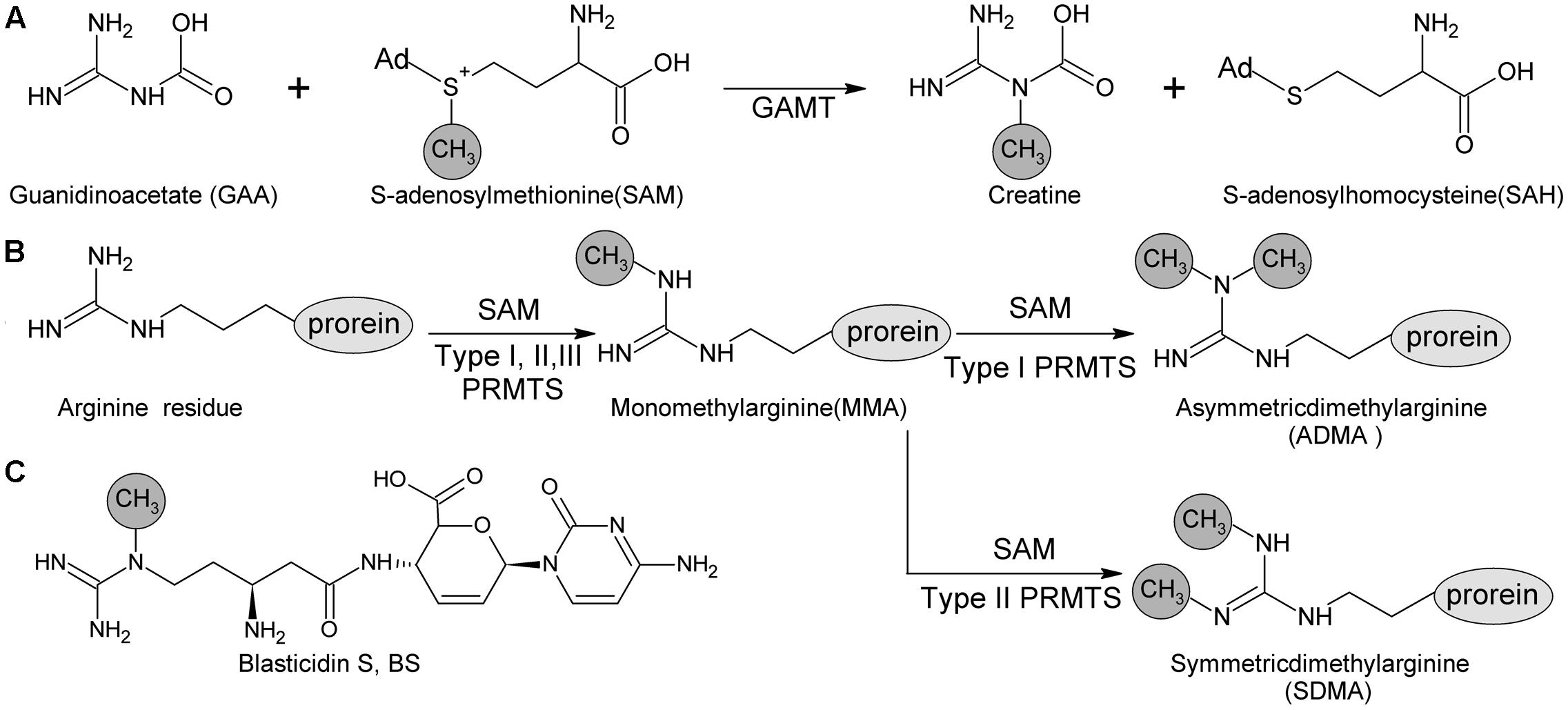



Frontiers Guanidine N Methylation By Blsl Is Dependent On Acylation Of Beta Amine Arginine In The Biosynthesis Of Blasticidin S Microbiology




Guanidino Group Is Present In The Amino Acid




Guanidine Png Images Pngegg



1
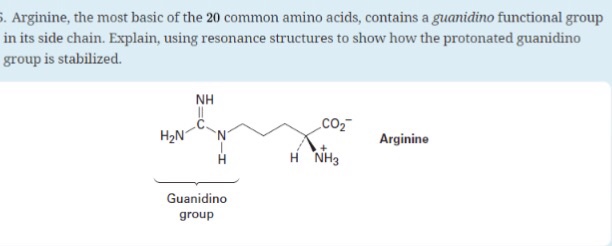



Solved Arginine The Most Basic Of The Common Amino Chegg Com
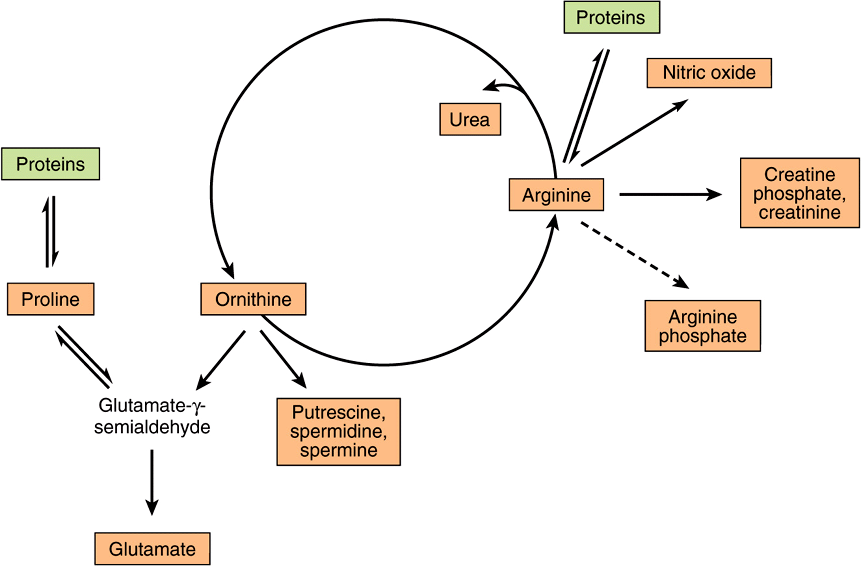



Conversion Of Amino Acids To Specialized Products Basicmedical Key




Exceptionally Versatile Arginine In Bacterial Post Translational Protein Modifications




Welcome To Chem Zipper Com What Is Guanidine And Its Structure Name Amino Acid Which Contains Guanidine Group




Lab 2 Color Tests For Proteins And Amino




Biochemistry Amino Acids Flashcards Quizlet




Amino Acid Standard Amino Acids Britannica




Bifunctional Guanidine Via An Amino Amide Skeleton For Asymmetric Michael Reactions Of B Ketoesters With Nitroolefins A Concise Synthesis Of Bicyclic B Amino Acids Yu 09 Angewandte Chemie International Edition




Guanidino Group An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Preparation And Characterization Of Co2 Responsive Poly Amino Acid Derivatives With Guanidine Group Springerprofessional De



Amino Acids And Proteins



No comments:
Post a Comment